SciPy Graphs
Working with Graphs
Graphs are an essential data structure.
SciPy provides us with the module scipy.sparse.csgraph for working with
such data structures.
Adjacency Matrix
Adjacency matrix is a nxn matrix where n
is the number of elements in a graph.
And the values represents the connection between the elements.
Example:
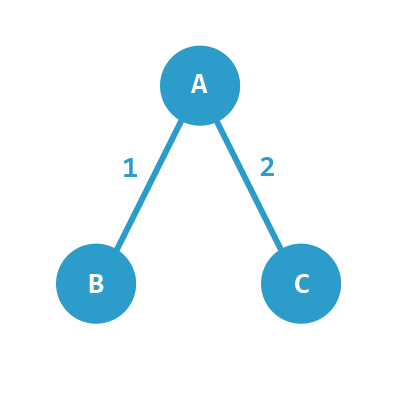
For a graph like this, with elements A, B and C, the connections are:
A & B are connected with weight 1.
A & C are connected with weight 2.
C & B is not connected.
The Adjency Matrix would look like this:
A B C
A:[0 1 2]
B:[1 0 0]
C:[2 0 0]
Below follows some of the most used methods for working with adjacency matrices.
Connected Components
Find all of the connected components with theconnected_components() method.
Example
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import connected_components
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.array([
[0, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 0],
[2, 0, 0]
])
newarr = csr_matrix(arr)
print(connected_components(newarr))
Try it Yourself »
Dijkstra
Use the dijkstra method to find the shortest path in a graph from one element to
another.
It takes following arguments:
- return_predecessors: boolean (True to return whole path of traversal otherwise False).
- indices: index of the element to return all paths from that element only.
- limit: max weight of path.
Example
Find the shortest path from element 1 to 2:
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import dijkstra
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.array([
[0, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 0],
[2, 0, 0]
])
newarr = csr_matrix(arr)
print(dijkstra(newarr, return_predecessors=True, indices=0))
Try it Yourself »
Floyd Warshall
Use the floyd_warshall() method to find shortest path between all pairs of elements.
Example
Find the shortest path between all pairs of elements:
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import floyd_warshall
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.array([
[0, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 0],
[2, 0, 0]
])
newarr = csr_matrix(arr)
print(floyd_warshall(newarr, return_predecessors=True))
Try it Yourself »
Bellman Ford
The bellman_ford() method can also find the shortest path between all pairs of elements, but this method can handle negative weights as well.
Example
Find shortest path from element 1 to 2 with given graph with a negative weight:
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import bellman_ford
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.array([
[0, -1, 2],
[1, 0, 0],
[2, 0, 0]
])
newarr = csr_matrix(arr)
print(bellman_ford(newarr, return_predecessors=True, indices=0))
Try it Yourself »
Depth First Order
The depth_first_order() method returns a depth first traversal from a node.
This function takes following arguments:
- the graph.
- the starting element to traverse graph from.
Example
Traverse the graph depth first for given adjacency matrix:
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import depth_first_order
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.array([
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1]
])
newarr = csr_matrix(arr)
print(depth_first_order(newarr, 1))
Try it Yourself »
Breadth First Order
The breadth_first_order() method returns a breadth first traversal from a node.
This function takes following arguments:
- the graph.
- the starting element to traverse graph from.
Example
Traverse the graph breadth first for given adjacency matrix:
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import breadth_first_order
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.array([
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1]
])
newarr = csr_matrix(arr)
print(breadth_first_order(newarr, 1))
Try it Yourself »


